Microsoft Windows 10 memory integrity, or "core isolation", uses hardware virtualization to protect memory used by Windows system processes from manipulation (often by malware). This is generally a good security feature to enable, though it may interfere with older device drivers. This option is not automatically turned on by some vendors, so you will need to check this yourself.
Read about Microsoft's Core Isolation.
A recently purchased MS Windows 10 chromebook from Dell had this option turned off, so Core Integrity should be checked even on factory-delivered machines. The Dell chromebook was runing the Windows version known as "Windows 10 Home in S mode".
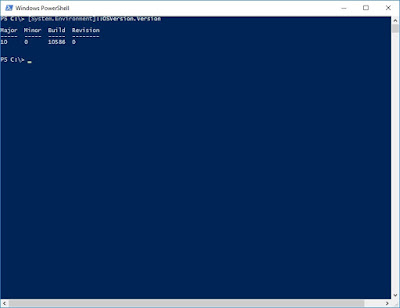
For any Windows 10, check if Windows is running with virtualization by looking in Task Manager. Press Start button, and type: task manager
Choose the Task Manager app.
In Task Manager, click the Performance tab, then CPU. Look in the lower right for Virtualization. In the following picture of Task Manager, hardware virtualization is enabled. Alternatively, open a command prompt, run systeminfo, and look for the Hyper-V line.
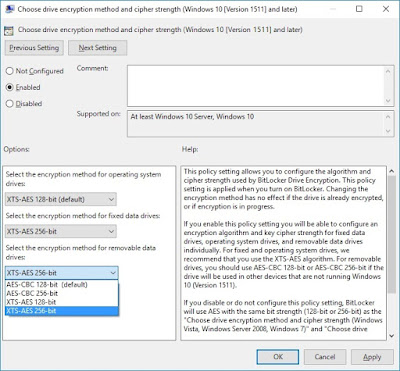
If Virtualization is not enabled, reboot the machine and press a key for BIOS setup (often a function key or the DEL key). In the BIOS setup utility, look for virtualization or "VT" and turn it on. Save the BIOS settings and restart the machine. Here are a couple different BIOS pictures:
After rebooting and starting Windows, go to the Settings app (press the Start button, press the gear icon). In the Settings app, type: core isolation
Pressing Core Isolation will open Windows Security, Device Security, and Core Isolation Details.
If you do not see Memory Integrity on the Core Isolation page, you will need to restart the computer and enter the BIOS settings to turn on virtualization options.
If Memory Integrity is already turned on, your machine is configured to use core memory integrity and your are done.
If Memory Integrity is off, try to turn it on. In some cases it will turn on easily. In other cases it will want a reboot. In more challenging cases it will find incompatible drivers and you can decide how to correct each driver.
For the following procedures, you will need to be the computer Administrator.
It may take a restart to fully set Core Isolation to on. If it finds incompatible drivers, press the Review link.
Some incompatible drivers must be completely removed. In one case, I encountered an incompatible Realtek sound driver that I removed, rebooted, turned on Memory Integrity, and then was able to reinstall the same sound driver while successfully keeping Memory Integrity turned on.
In this example, the Realtek sound driver and the ViMicro web cam drivers are incompatible. To remove these drivers, look in device manager and uninstall the drivers. As computer Administrator, press Start button and type: device manager
Look around in Device Manager for the yellow flags, and try to update or uninstall the device and delete the driver software. In this case, the old driver "oem3.inf" could not be removed through Device Manager.
The driver was able to be removed from the command line as Administrator: pnputil /delete-driver oem3.inf
If a driver will not uninstall, you can also remove it by hand (or rename it). Look in folder C:\Windows\System32\drivers.
When done resolving incompatible drivers, the Memory Integrity setting in Windows Security Center should look like this.
When finished, you may want to create a restore point. Press the Start button and type: restore point
Configure and Create the new restore point.
You should now check for corrupt Windows files. This will run the Windows Module Installer and verify and correct the Windows software.